Early Life and Ascension to Power
Mansa Musa, also known as Musa I of Mali, was born in 1280 and ascended the throne in 1312. He became the 10th Mansa, or emperor, of the Mali Empire, a West African state that flourished during the 13th and 14th centuries. The Mali Empire was rich in natural resources, particularly gold, which significantly contributed to Musa’s immense wealth.
Mansa Musa came to power following the previous emperor, Abu-Bakr II, who embarked on a voyage across the Atlantic and never returned. Musa was appointed deputy during Abu-Bakr’s absence and assumed the throne after his disappearance.
The Wealth of Mali
Under Mansa Musa’s rule, the Mali Empire reached its zenith in terms of territory, wealth, and cultural influence. The empire encompassed present-day Mali, Senegal, Gambia, Guinea, Niger, Nigeria, Chad, and Mauritania. The region was rich in gold mines, particularly in Bambuk, Boure, and Galam. Mali’s strategic position in the trans-Saharan trade routes further enhanced its wealth, as it became a key player in the exchange of gold, salt, and other goods.
Mansa Musa’s wealth is often considered the largest in history. Although estimates vary, modern historians suggest that his personal fortune, adjusted for inflation, could be worth around $400 billion today. His wealth was not just personal but also reflected the prosperity of his empire, which thrived under his reign.
The Famous Pilgrimage to Mecca
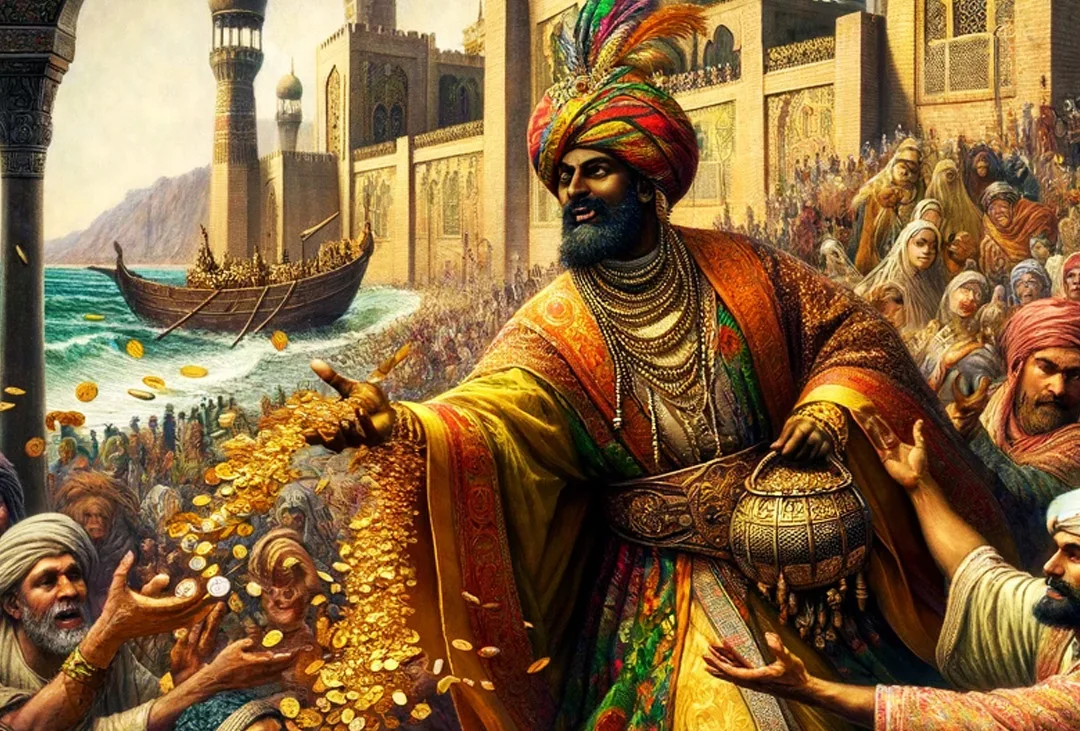
One of the most famous events during Mansa Musa’s reign was his pilgrimage (Hajj) to Mecca in 1324. This journey, spanning over 4,000 miles, was not just a religious obligation but also a demonstration of his wealth and power. Mansa Musa traveled with a grand entourage that included thousands of soldiers, attendants, and slaves, as well as camels and horses laden with gold.
Mansa Musa’s pilgrimage had a significant impact on the regions he passed through. In Cairo, for instance, his lavish spending and generous gifts of gold caused inflation that took years to stabilize. The gold he distributed devalued the precious metal in Egypt and other parts of the Middle East, showcasing the sheer scale of his wealth.
Cultural and Educational Contributions
Beyond his wealth, Mansa Musa is remembered for his contributions to culture and education. Upon his return from Mecca, he brought with him architects, scholars, and artisans. This influx of knowledge and skills led to a golden age in Mali.
Mansa Musa commissioned the construction of numerous buildings, including the famous Djinguereber Mosque in Timbuktu, which became an epicenter of learning and culture. Timbuktu flourished under his patronage, becoming a renowned center for Islamic learning, attracting scholars from across the Muslim world. The city’s libraries and universities made it one of the most important intellectual hubs of the medieval period.
Legacy
Mansa Musa’s reign left an indelible mark on the history of West Africa and the world. His display of wealth during his pilgrimage significantly enhanced the global perception of Mali, putting it on the map as a land of immense riches and cultural sophistication. The educational and architectural advancements he initiated had a lasting impact, fostering a legacy of learning and cultural richness in Mali.
Today, Mansa Musa is often cited as one of the richest individuals in history. His story is a testament to the grandeur and prosperity of the Mali Empire during the 14th century and remains a powerful symbol of African heritage and achievement.