The Mayan civilization stands as one of the most sophisticated and mysterious cultures of the ancient world. Flourishing in Mesoamerica — encompassing present-day southern Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, and El Salvador — the Mayans created a remarkable society known for its architectural, mathematical, astronomical, and linguistic achievements. Spanning over 3,000 years, from as early as 2000 BCE to the Spanish conquest in the 16th century, the civilization left behind a legacy still being unraveled today.
Origins and Development
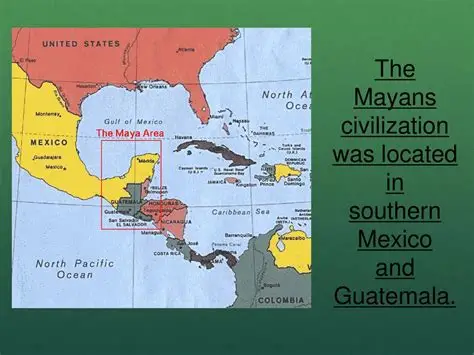
The roots of the Mayan civilization can be traced back to the Preclassic Period (2000 BCE–250 CE). Early agricultural communities began to organize into complex societies, with the Olmecs often seen as precursors. The Mayans inherited and further developed many aspects of Olmec culture, including ceremonial architecture and calendrical systems.
By the Classic Period (250–900 CE), the Maya had reached the peak of their cultural and political development. City-states such as Tikal, Calakmul, Palenque, Copán, and Caracol became powerful centers of governance, trade, religion, and warfare. Each city-state was ruled by a king (or k’uhul ajaw) believed to be divinely sanctioned.
Scientific and Cultural Achievements

The Mayans were pioneers in numerous fields:
- Astronomy and Calendars: They developed highly accurate calendars — including the Tzolk’in (260-day ceremonial calendar) and the Haab’ (365-day solar calendar) — and were able to predict solar eclipses and planetary movements. The Long Count calendar famously led to myths about the world ending in 2012.
- Mathematics: The Maya independently developed the concept of zero, an advanced mathematical concept that allowed for complex calculations.
- Writing System: The Mayans created the most sophisticated writing system in pre-Columbian Americas, using over 800 glyphs to represent sounds, objects, and ideas. These inscriptions can be found on stelae, pottery, and codices (folding books made of bark paper).
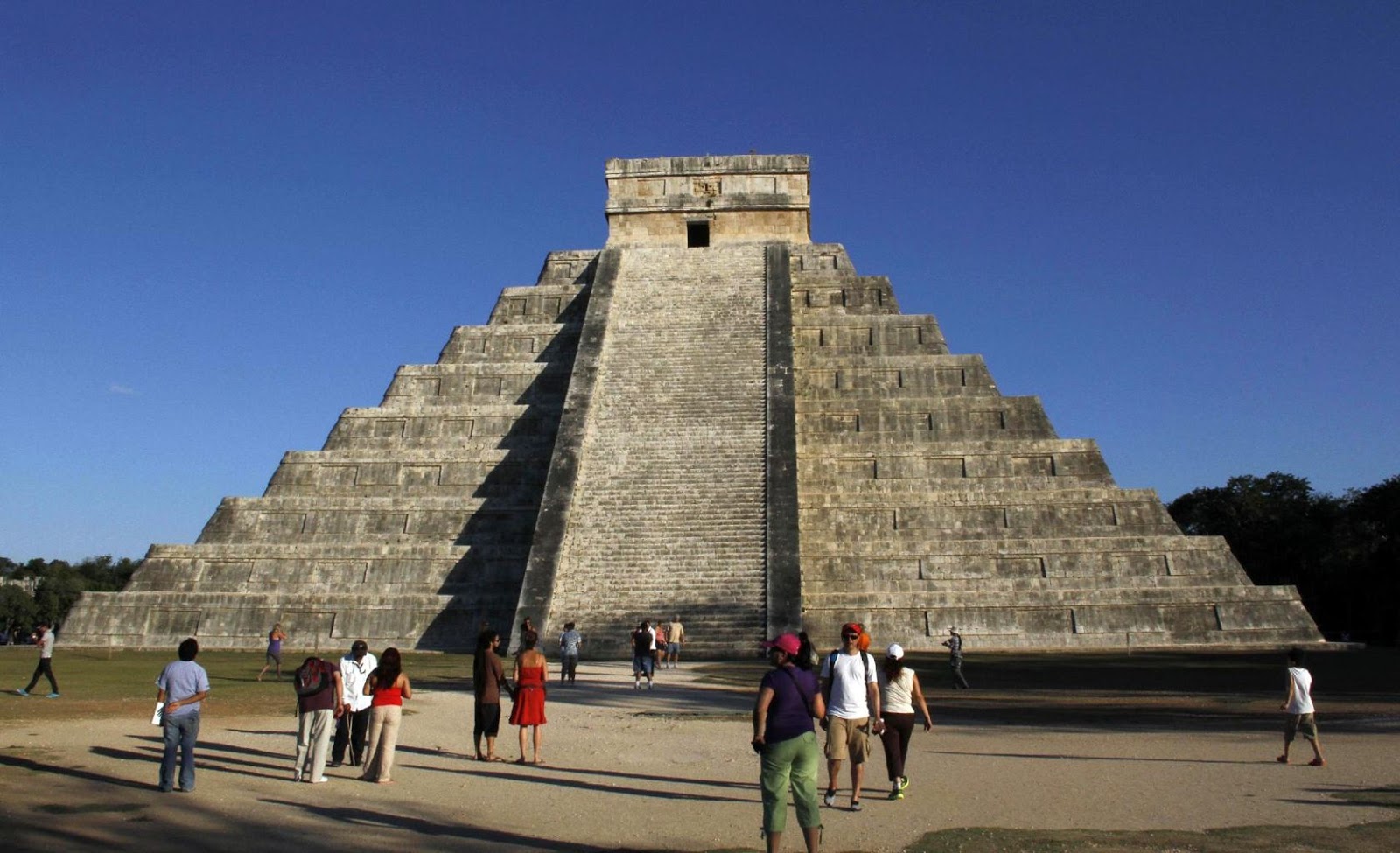
- Architecture: They built towering pyramids, grand palaces, and ceremonial ball courts. Structures like the Pyramid of Kukulcán at Chichén Itzá and the Temple of the Inscriptions at Palenque remain architectural marvels.
- Art and Religion: Mayan art — including pottery, sculpture, and murals — was deeply tied to religious beliefs and cosmology. Their polytheistic religion worshiped gods related to nature, astronomy, and agriculture, and involved elaborate rituals, including human sacrifices.
Society and Economy
Mayan society was highly stratified. At the top were kings and nobles, followed by scribes, artisans, traders, farmers, and laborers. The economy was primarily agrarian, based on maize cultivation, but also included extensive trade in jade, obsidian, cacao, salt, and textiles. Markets and long-distance trade routes connected various parts of the region.
Decline and Legacy
The “Classic Maya Collapse” around 900 CE remains one of history’s enduring mysteries. Many southern cities were abandoned, leading to a population shift to the northern lowlands, where cities like Chichén Itzá rose to prominence. Scholars suggest a combination of factors including warfare, environmental degradation, droughts, and political upheaval contributed to the decline.
Despite the arrival of Spanish conquistadors in the 16th century and the violent suppression of indigenous culture, millions of Mayan descendants still live in Central America today. Many continue to speak Mayan languages, maintain traditions, and preserve cultural knowledge passed down through generations.
Conclusion
The Mayan civilization was not only a marvel of its time but also a testament to human ingenuity and resilience. Its cities may have fallen into ruin, but its legacy endures through archaeology, language, and the living cultures of its descendants. As new discoveries continue to emerge, the story of the Maya grows richer, reminding us of the depth and complexity of ancient human civilizations.


Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://accounts.binance.com/sl/register-person?ref=I3OM7SCZ